Our autism support classrooms provide individualized instruction to students with mild to severe global delays associated with an autism spectrum disorder. Class sizes are small, no more than eight students per room, with a high adult to student ratio. Our educational program promotes communicative, behavioral, social, emotional, academic, motor, adaptive and independent living skills.
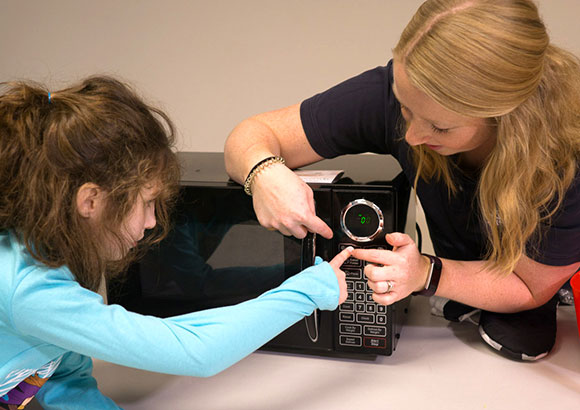

Instruction
Students demonstrating skill deficits in areas of expressive language, social pragmatics, activities of daily living, occupational skills, reciprocal social interactions, safety awareness and/or independence across environments in their lives receive intensive instruction evidenced to increase these skills and improve academic performance. Verbal Behavior Milestones Assessment and Placement Program (VB-MAPP) or Essentials for Living (EFL) assessments and programming are often utilized to design instruction for students demonstrating these skills deficits.
Learning is individualized, so those students who show deficits in areas of social-emotional skills, complex social relationships and/or reciprocal social interactions receive instruction through differentiated instruction using standards aligned curriculum infused with social skills programming and social-emotional learning.
We offer supports for all levels of programming, including visual teaching tools, intensive social skills instruction, and individualized academic programs. These individualized academic programs include functional reading, functional writing, functional math, self-help, vocational and community awareness and safety, and specialized physical education activities. Classroom activities emphasize all areas of a student’s development, including communication, language, socialization, school readiness, self-care, and play skills.
Learning Environments
Our schools enhance learning opportunities using specially designed spaces. These spaces include sensory rooms, life skills apartments, vocational labs, natural environment teaching (NET) areas, therapy rooms, and gross motor movement areas.
State of the art multi-sensory environments (MSE) are a dedicated space where sensory integration can be controlled through a range of visual, auditory, olfactory and tactile stimuli. As students are taught how to interact with each stimulus, they experience calming effects, stimulation, socialization, improved focus, and further development with motor skills, cognition and sensory management.
Vocational labs allow students to prepare for future employment opportunities by learning pre-vocational skills through a variety of stations and activities. Many of these spaces include office work, service industry activities such as setting tables and bussing, retail store functions such as stocking shelves and using the cash register, and manufacturing activities such as assembly line and packaging.
Functional life skills apartments allow students to learn vital independent skills for adulthood in a realistic home setting. In these spaces, students can sort, launder, and fold clothes, cook meals, wash dishes, make a bed, and engage in leisure activities.
Terms You Will Hear
-
Verbal Behavior
Verbal behavior instruction focuses on the function of language over the structure of language. Instead of focusing on verbs, adjectives, and nouns as the primary way to teach communication, verbal behavior focuses on how those words or other communicative actions impact the person and their environment.
-
Differentiated Instruction
Recognizing each student has individualized strengths and needs, differentiated instruction requires teachers to know their students and provide each one with experiences and tasks tailored to improve their learning. Components of DI include teaching with diverse materials, organizing instruction to meet all learner levels and using individual and small-group instruction.
-
Social Skills Instruction
Weekly and daily instruction focuses on teaching students specific behaviors to enhance their social interaction toolbox. Topics include active listening, following directions, meeting new people and more. Instruction follows the Tell-Show-Do-Review model to engage students in active learning.
-
Sensory Integration
A form of occupational therapy to help children with sensory-processing problems cope with the difficulties they have processing sensory input. Techniques are used to strengthen the student’s sense of touch (tactile), sense of balance (vestibular), and a sense of where the body and its parts are in space (proprioceptive).
-
Life Skills Instruction
Life skills instruction equips students with the skills to thrive in the world beyond the classroom. Teaching practical activities of daily living and independence skills enables students to leave school and contribute to their communities and society.
-
Pre-Vocational Instruction
This instructional process takes larger vocational tasks and teaches them in smaller steps using recognizable materials to help students learn faster and with greater accuracy.
-
Natural Environment Teaching (NET)
NET is a group of practices used to encourage the development of communication in social settings based on the student’s interests. Teaching in the natural environment through daily routines promotes skill development in communication and socialization.
-
Intensive Teaching Trials (ITT)
Based upon Applied Behavior Analysis principles, ITT provides students many opportunities for responding during each session resulting in faster learning. Critical components of ITT include a brisk pace of instruction, mixing and varying tasks, interspersing hard and easy tasks and reduction of incorrect responses through errorless correction.